Abstract
Introduction: Economic analyses in health research often needs outcomes assessed as a single number - a health utility score - defined by anchors of perfect health = 1 and death = 0. Two survey-based health utility measures are the EQ-5D and the SF-6D. The SF-6D is derived from responses to the SF-36® Health Survey (SF-36). Utility scores have been derived separately for each measure by analyses of preferences for different health states, but the two measures often give different results. For this reason, mapping algorithms have been developed to directly predict EQ-5D scores from the SF-36. We aimed to evaluate whether existing SF-36-to-EQ-5D mapping algorithms are appropriate for AL amyloidosis patients in clinical trials.
Methods: As part of a non-interventional, longitudinal study, patients with AL amyloidosis completed online surveys which assessed demographics, disease and treatment characteristics, as well as health-related quality of life. Patients also reported specific organ involvement on the initial survey using a checklist of organs/systems commonly affected by AL amyloidosis: heart, kidney, liver, nervous system, gastrointestinal system. Patients were asked to complete the SF-36v2 and the EQ-5D (3 Level) during round 5 of data collection (18 months following the initial survey). Scores for SF-36v2 subscales, SF-6D and EQ-5D were calculated according to the survey developer's procedures. For all patients with complete subscale scores (n=184), predicted EQ-5D scores (EQ-5D-P) were calculated based on an algorithm from Rowen et al (2009). Score means, 95% confidence intervals (95%CI), standard deviations (SD), ceiling and floor effects were compared in the overall sample and in subgroups defined by self-rated disease impact (as measured by the Patient Global Impression Severity Scale [PGI-S]). Random error was evaluated in terms of mean absolute error (MAE) and mean square error (MSE). Evaluation of health impact was performed in relation to organ involvement and reported as regression parameters and 95%CI.
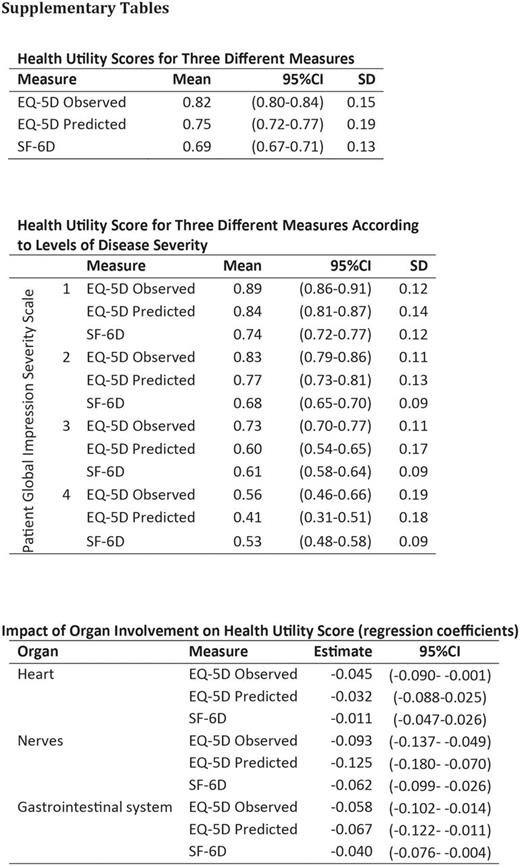
Results: Health utility scores differed significantly between measures, with the EQ-5D having the highest scores (Mean= 0.82, 95%CI = (0.80 - 0.84), SD = 0.15), followed by EQ-5D-P (= 0.75 (0.72 - 0.77), 0.19) and SF-6D (= 0.69 (0.67 - 0.71), 0.13). EQ-5D also had the strongest ceiling effect (27% vs. 0% and 1%). None of the measures showed floor effects. Compared to the EQ-5D, random error was smaller for EQ-5D-P (MAE=0.11, MSE=0.02) than for SF-6D (MAE=0.15, MSE=0.03). Based on the PGI-S subgroup analyses, EQ-5D scores were higher than EQ-5D-P in all subgroups (0.89/0.84, 0.83/ 0.77, 0.73/0.60, 0.56/0.41). The three scores provided different assessments of the impact on health utility of heart involvement (EQ-5D: β=-0.045 (95%CI = -0.090 - -0.001) , EQ-5D-P:-0.032 (-0.088 - 0.025), SF-6D: -0.011 (-0.047 - 0.026)), nerve involvement (EQ-5D:-0.093 (-0.137 - -0.049) , EQ-5D-P: -0.125 (-0.180 - -0.070), SF-6D: -0.62 (-0.099 - -0.026)), and gastrointestinal involvement (EQ-5D:-0.058 (-0.102 - -0.014) , EQ-5D-P: -0.067 (-0.122 - -0.011), SF-6D: -0.040 (-0.076 - -0.004)).
Conclusion: Two standard health utility measures, EQ-5D and SF-6D, provided different health utility values for AL amyloidosis patients and different assessments of the burden of specific disease complications. An EQ-5D prediction algorithm provided results that were in between the two measures, but the prediction of the EQ-5D was not well targeted for AL amyloidosis patients. To successfully predict EQ-5D scores in AL amyloidosis patients, a disease specific prediction algorithm needs to be developed.
Reference
Rowen, D., Brazier, J., & Roberts, J. (2009). Mapping SF-36 onto the EQ-5D index: how reliable is the relationship? Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 7 (1), 27.
McCausland: Prothena Biosciences: Research Funding; Optum: Employment. Bjorner: Prothena Biosciences: Research Funding; Optum: Employment. Quock: Prothena Biosciences Inc: Employment, Other: Stockholder. White: Optum: Employment; Prothena Biosciences: Research Funding. Bayliss: Optum: Employment; Prothena Biosciences: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal